My first: Item: Difference between revisions
m (Protected "My first: Item" ([Edit=⧼protect-level-larianeditonly⧽] (indefinite) [Move=⧼protect-level-larianeditonly⧽] (indefinite))) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
The physical map (PM) channels are as follow: <br /> | The physical map (PM) channels are as follow: <br /> | ||
* Roughness in green (G) channel | * Roughness in green (G) channel | ||
* Metalness in | * Metalness in red (R) channel | ||
* Ambient Occlusion is in | * Ambient Occlusion is in blue (B) channel | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Revision as of 08:59, 24 September 2018
Welcome to the Items guide. Here you will find the item creation pipeline from modelling to importing your item in Divinity Engine 2.
This article is part of a collection of guides, with a page for every type of item.
| General |
| Scenery (Rocks, plants, trees, shelves, etc.) |
| Lootable items (Shells, plates, food, gems, etc.) |
| Interactable animated items (Levers, doors, etc.) |
| Interactable socket items (Chairs, beds, etc.) |
| Weapons (The sharp stuff) |
To create items you will need some 3d modelling and texturing skills.
Two most important things you need to have if you want to create an Item: item model and it's textures.
File formats
In the editor 3d models are saved as granny files (.GR2).
The textures are saved as DirectDraw Surface (.dds).
| More info on Granny 3D can be found here |
| More info on DirectDraw Surface can be found here |
No matter what type of item you want to do your pipeline will consists of:
- Modelling
- Texturing
- Setting up the item in the file
- Setting up the item in the editor
Modelling
You will need a 3d modelling software to create items. If you unfamiliar with 3d modelling we advice you to check some 3d modelling specific guides first.
Places you can find good tutorials about 3d modelling:
- Polycount
- Cubebrush
- YouTube tutorials (good example)
Importing your resources in the editor
If you already have your granny files (.GR2) and Direct Draw Surface (.dds) texture files it's time to import them in the editor.
- Open your Content Browser. Choose a correct package or create a new one.
- Hit the add resource button (highlighted red in the left upper corner) and select what type of resource you want to add.
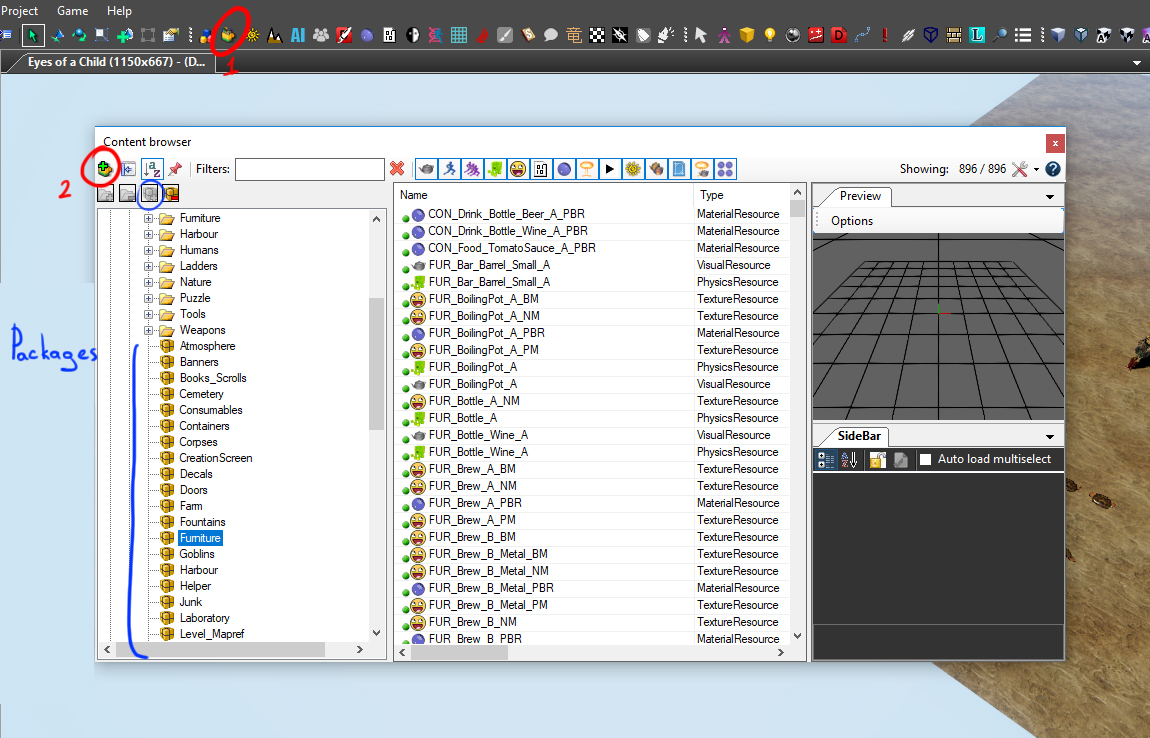
After that you'll need to make a new material, assign textures to your new material and assign the material to your mesh.
To make a new material you have two options:
- Create a new material by pressing "Add resource" button highlighted red on the screenshot above and select material.
- Select any material that you see in content browser right click it and select "Create new from selected". That will create a new material copy with all settings from the original.
Now you need to assign textures to your material and material to the mesh.
Depending on the type of the material you're using it can have different texture parameters.
The most standard material we use for items is called Base_PBR.
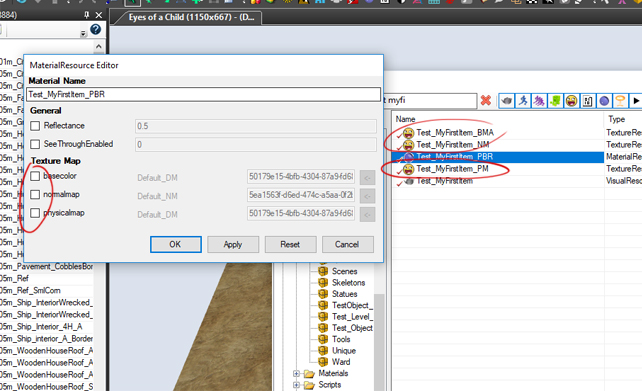
We are using physical based rendering, it means that you need a base color texture (BM) a physical map (PM) and a normal map (NM)
The physical map (PM) channels are as follow:
- Roughness in green (G) channel
- Metalness in red (R) channel
- Ambient Occlusion is in blue (B) channel
See also
| General |
| Scenery (Rocks, plants, trees, shelves, etc.) |
| Lootable items (Shells, plates, food, gems, etc.) |
| Interactable animated items (Levers, doors, etc.) |
| Interactable socket items (Chairs, beds, etc.) |
| Weapons (The sharp stuff) |